How to print colour print – Step into the world of color printing, where vibrant hues and crisp details come to life. From understanding different printing technologies to mastering color management, this comprehensive guide will empower you to achieve stunning color prints that meet your every need.
Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting your journey into the world of color printing, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and techniques you need to create exceptional prints that will captivate your audience.
Introduction to Color Printing
Color printing is a process of reproducing an image or text in color, rather than in black and white. It involves combining different amounts of cyan, magenta, yellow, and black (CMYK) inks to create a wide range of colors.Color printing is used in a variety of applications, including:* Commercial printing:Color printing is used to produce magazines, brochures, posters, and other marketing materials.
Fine art printing
Color printing is used to produce high-quality reproductions of paintings, photographs, and other works of art.
Textile printing
To print in color, ensure your printer supports color printing and has compatible ink cartridges. If you encounter issues while printing in color, it may be necessary to troubleshoot your printer. For instance, if you’re experiencing difficulties removing your HP printer from HP Smart, refer to how to remove hp printer from hp smart for guidance.
After resolving any printer issues, you can resume printing in color by selecting the appropriate color settings in your printing software.
Color printing is used to produce fabrics with colorful patterns.
Packaging
Color printing is used to produce colorful packaging for products.There are a number of different color printing technologies, including:* Offset printing:Offset printing is a traditional printing process that uses metal plates to transfer ink to paper.
Digital printing
Digital printing is a newer printing process that uses digital files to create images on paper.
Inkjet printing
Inkjet printing is a type of digital printing that uses small drops of ink to create images on paper.
Laser printing
Laser printing is a type of digital printing that uses a laser to create images on paper.The choice of color printing technology depends on a number of factors, including the desired print quality, the size of the print run, and the budget.
Color Printing Methods
Color printing refers to the process of reproducing a physical image using multiple colors. It is commonly used for various purposes, including graphic design, photography, and commercial printing.
Several color printing methods are available, each with its advantages and disadvantages. The most common methods include inkjet, laser, and thermal printing.
Inkjet Printing
Inkjet printing is a non-impact printing technology that uses tiny droplets of ink to create an image. Inkjet printers have a printhead that moves across the paper, depositing ink droplets to form the desired image.
Inkjet printing offers high-quality prints with excellent color accuracy and detail. However, inkjet printers can be slower and more expensive than other printing methods.
Laser Printing
Laser printing is an electrostatic printing technology that uses a laser beam to create an image on a photosensitive drum. The drum then transfers the image to paper using toner particles.
Laser printing offers fast and cost-effective printing with sharp text and graphics. However, laser printers can produce less vibrant colors compared to inkjet printers.
Thermal Printing
Thermal printing is a non-impact printing technology that uses heat to create an image on specially coated paper. Thermal printers have a printhead that contains tiny heating elements that selectively heat the paper to produce the desired image.
Thermal printing is a fast and inexpensive printing method, but it offers lower print quality compared to inkjet and laser printing.
Color Printer Selection

Selecting the right color printer is crucial for meeting specific printing needs. Consider the following factors:
Print Volume
Estimate the number of pages printed monthly. Low-volume printers are suitable for occasional use, while high-volume printers can handle large print jobs.
Print Quality
Determine the desired print quality. Higher resolutions produce sharper images and text, but may come at a higher cost.
Cost
Consider the initial purchase price, ongoing ink costs, and maintenance expenses. Laser printers generally have lower ink costs, while inkjet printers offer more vibrant colors.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Inkjet | Laser |
|---|---|---|
| Print Volume | Low to medium | High |
| Print Quality | Vivid colors | Crisp text |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, higher ink costs | Higher initial cost, lower ink costs |
Troubleshooting Common Color Printing Problems
- Faded or dull colors:Check ink levels and replace empty cartridges.
- Streaks or lines:Clean the print heads or replace the ink cartridges.
- Misaligned colors:Adjust the printer settings or contact technical support.
Sample Email to a Customer
Dear [Customer Name],
Thank you for your inquiry about color printers. Based on your estimated print volume and desired print quality, I recommend the following options:
- [Printer 1] for low-volume, high-quality printing
- [Printer 2] for medium-volume, cost-effective printing
- [Printer 3] for high-volume, professional-grade printing
Please let me know if you have any further questions. We are happy to assist you in finding the perfect color printer for your needs.
Sincerely,
[Your Name]
Color Management for Printing
Color management is critical in printing to ensure accurate and consistent color reproduction across different devices and media. Without proper color management, colors may appear different on the screen compared to the printed output, leading to dissatisfaction and costly reprints.
Accurate color reproduction involves managing the entire workflow from image capture to printing, considering factors such as:
- Camera calibration: Ensuring the camera accurately captures colors.
- Monitor calibration: Calibrating the monitor to display colors accurately.
- Printer calibration: Calibrating the printer to produce consistent colors.
- Color profiles: Creating and using color profiles that define the color characteristics of devices and media.
- Proofing: Creating physical proofs to verify color accuracy before mass printing.
Techniques for Accurate Color Reproduction
Techniques for accurate color reproduction include:
- Using color profiles:Color profiles are essential for accurate color reproduction. They contain information about the color characteristics of a specific device or media, allowing software and devices to interpret and reproduce colors consistently.
- Calibrating devices:Calibrating devices such as cameras, monitors, and printers ensures they produce and display colors accurately. This involves using specialized software and equipment to adjust the devices’ color settings.
- Proofing:Proofing involves creating physical prints to verify color accuracy before mass printing. Proofs can be used to identify and correct any color issues before committing to a large print run.
Paper and Ink for Color Printing

Selecting the right paper and ink combination is crucial for achieving optimal color printing results. Paper and ink properties can significantly impact the vibrancy, accuracy, and longevity of printed colors.
When choosing paper, consider the following factors:
Paper Types
- Brightness:Measured in percentage, indicates the paper’s whiteness. Higher brightness enhances color contrast and vibrancy.
- Thickness:Expressed in pounds per ream (lb), determines the paper’s weight and durability. Thicker paper resists curling and is suitable for high-quality prints.
- Surface texture:Glossy, matte, and satin finishes affect color appearance. Glossy surfaces produce vibrant colors, while matte finishes provide a more subdued look.
Ink formulations also play a vital role in color printing:
Ink Formulations
- Dye-based inks:Water-soluble and produce vibrant colors. However, they are less resistant to fading and moisture.
- Pigment-based inks:Particle-based and provide excellent color accuracy and longevity. They are water-resistant and less prone to fading.
The following table compares different paper and ink combinations to illustrate their effects on print quality:
| Paper | Ink | Color Gamut | Longevity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glossy | Dye-based | Wide | Low |
| Matte | Dye-based | Narrow | Low |
| Glossy | Pigment-based | Wide | High |
| Matte | Pigment-based | Narrow | High |
For specific printing applications, consider the following:
- Fine art:Pigment-based inks on archival-quality paper ensure color accuracy and longevity.
- Photography:Glossy paper with dye-based inks produces vibrant colors for display prints.
- Commercial printing:Pigment-based inks on coated paper provide durability and color consistency for mass production.
Troubleshooting Color Printing Issues: How To Print Colour Print
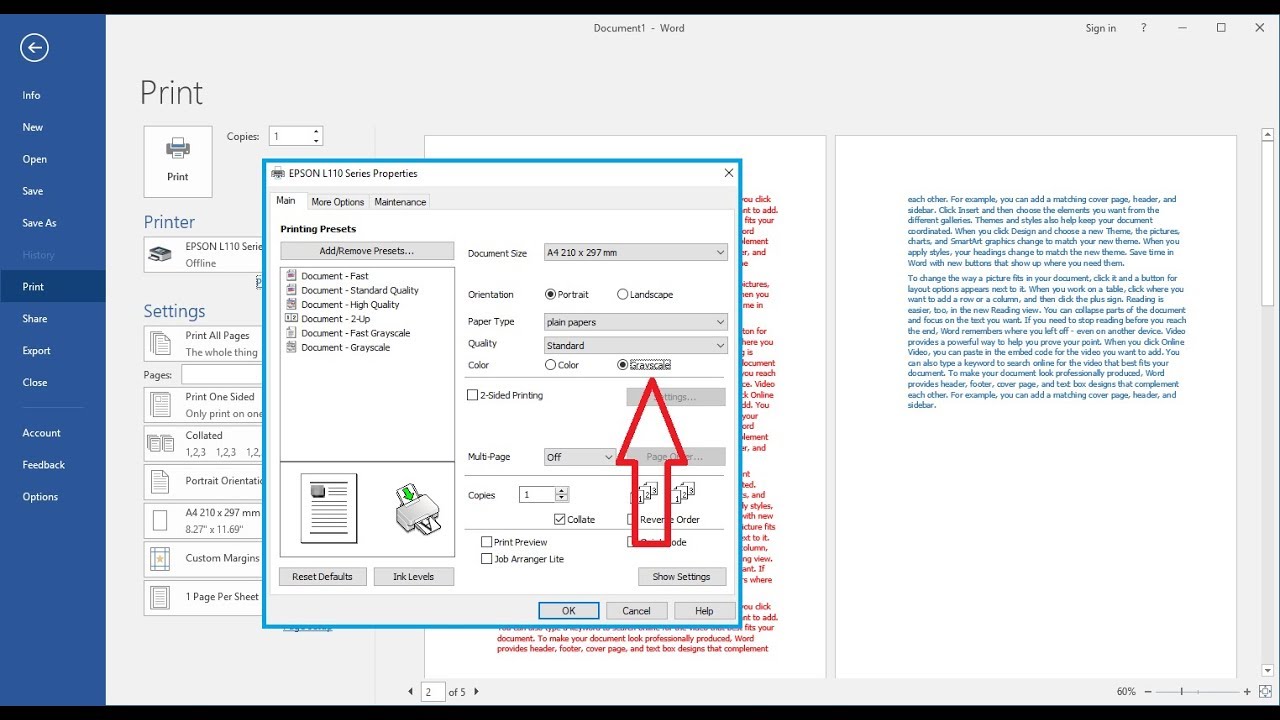
Color printing issues can arise from various factors, including printer hardware, software, and settings. Identifying and resolving these problems can enhance print quality and save time and resources.Common color printing problems include misaligned colors, incorrect color reproduction, banding or streaking, and faded or dull prints.
These issues can be caused by factors such as incorrect color profiles, clogged print heads, or low ink levels.
Advanced Color Printing Techniques
Advanced color printing techniques extend the capabilities of standard printing methods, offering greater control over color reproduction and enabling specialized printing applications.
Two notable advanced techniques are spot color printing and overprinting, each with its unique benefits and applications.
Spot Color Printing
Spot color printing utilizes pre-mixed, custom inks to achieve specific colors that cannot be reproduced using standard CMYK printing. This technique provides precise color matching and consistency, making it ideal for branding, packaging, and high-end print materials.
- Advantages of Spot Color Printing:
- Accurate color reproduction
- Consistency across different print runs
- Vivid and impactful colors
Overprinting
Overprinting involves printing multiple layers of ink on top of each other, creating new colors or effects. This technique is often used to create rich, saturated colors, simulate metallic or fluorescent effects, or add texture to prints.
- Advantages of Overprinting:
- Extended color gamut
- Creation of special effects
- Enhanced depth and dimension in prints
Cost-Effective Color Printing
Color printing can be an expensive endeavor, but there are several ways to reduce the cost without sacrificing quality. By optimizing print settings, minimizing ink consumption, and choosing the right paper and ink, you can significantly lower your color printing expenses.
Here are some tips for cost-effective color printing:
Print Settings Optimization
- Use Draft or Economy Mode:Most printers offer a draft or economy mode that uses less ink and produces lower-quality prints. This mode is suitable for documents that don’t require high-quality printing, such as drafts or internal memos.
- Reduce Print Resolution:The higher the print resolution, the more ink is used. For non-critical documents, consider reducing the print resolution to 300 dpi or less.
- Print in Grayscale:If color is not essential, consider printing in grayscale instead. This can save a significant amount of ink, especially when printing large documents.
Ink Consumption Minimization
- Use High-Capacity Ink Cartridges:High-capacity ink cartridges hold more ink and can significantly reduce the cost per page. While they may be more expensive upfront, they can save money in the long run.
- Monitor Ink Levels:Regularly check ink levels and replace cartridges when they are low to avoid running out of ink during a print job. Running a printer with empty cartridges can damage the print head and increase ink consumption.
- Clean Print Heads:Clogged print heads can waste ink and produce poor-quality prints. Regularly clean the print heads to ensure optimal ink flow and minimize ink consumption.
Paper and Ink Selection
- Choose the Right Paper:Different types of paper absorb ink differently. For color printing, use high-quality paper that is designed for color printing. This will help reduce ink bleeding and produce more vibrant colors.
- Use Compatible Ink:Using compatible ink can save money compared to using original manufacturer ink. However, ensure that the compatible ink is of good quality and compatible with your printer to avoid damaging the print head.
- Consider Refilling Ink Cartridges:Refilling ink cartridges is a cost-effective way to extend their lifespan. However, it requires some technical knowledge and may not be suitable for all printers.
Design Considerations for Color Printing

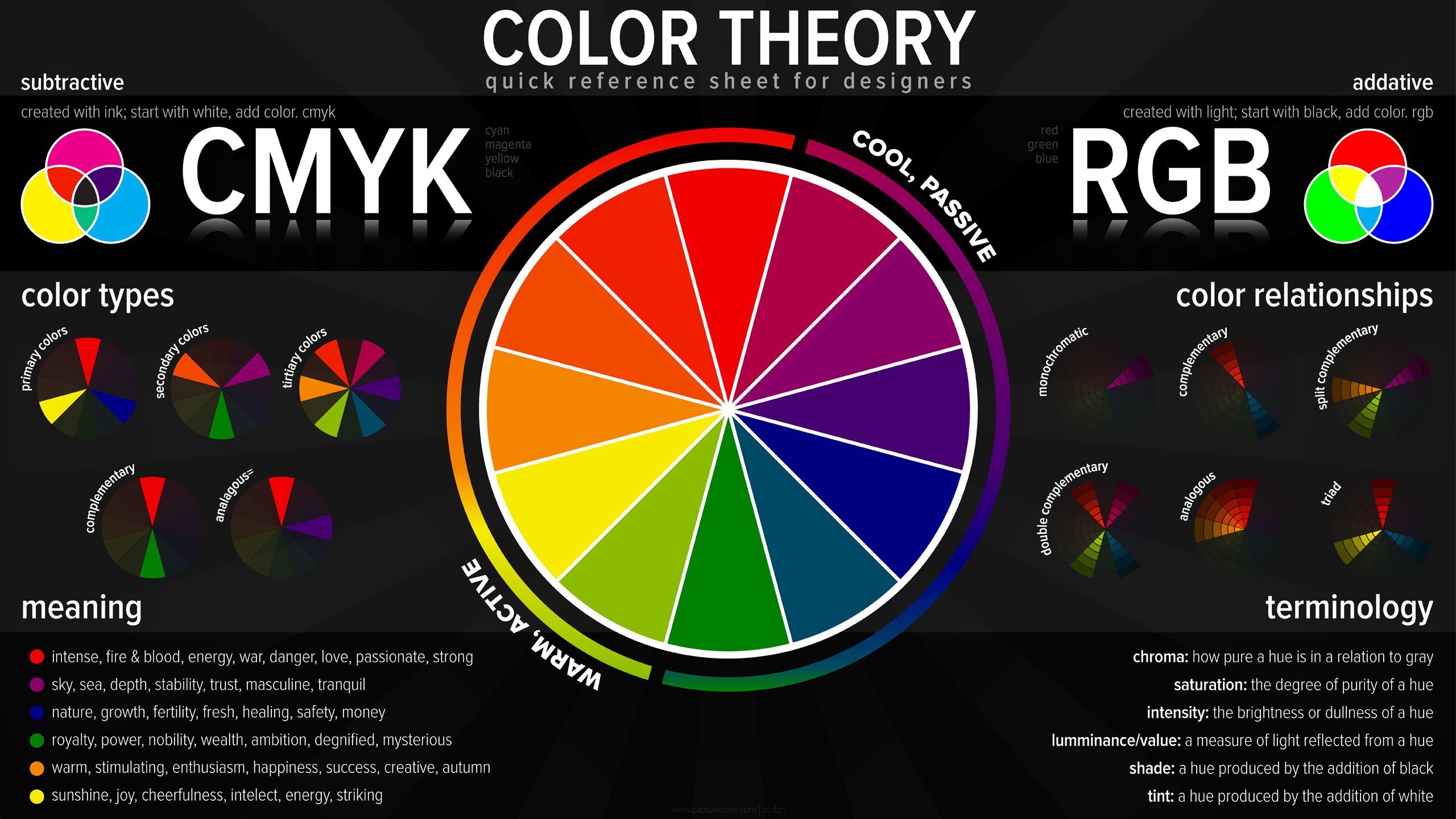
Design considerations are crucial for producing visually appealing and effective color prints. Color theory provides a framework for understanding how colors interact, and applying these principles ensures harmonious and impactful color choices.
Choosing Colors
- Color Wheel:The color wheel is a fundamental tool for selecting colors. It consists of primary (red, yellow, blue), secondary (green, orange, violet), and tertiary colors (combinations of primary and secondary colors).
- Complementary Colors:Colors opposite each other on the color wheel (e.g., red and green) create high contrast and visual impact when placed side by side.
- Analogous Colors:Colors adjacent to each other on the color wheel (e.g., blue, blue-green, green) create a harmonious and cohesive effect.
- Triadic Colors:Colors equidistant on the color wheel (e.g., red, yellow, blue) provide a vibrant and balanced color scheme.
Creating Color Palettes
A color palette is a carefully selected group of colors that work well together. When creating a color palette:
- Consider the Purpose:Determine the desired mood, tone, and message of the printed material to guide color selection.
- Limit the Number of Colors:Stick to a few main colors to maintain visual clarity and avoid overwhelming the viewer.
- Ensure Contrast:Choose colors with sufficient contrast to ensure legibility and visual interest.
Optimizing Color Contrast
Color contrast is essential for creating visually appealing and readable printed materials:
- Lightness Contrast:Use colors with different lightness values (e.g., light blue and dark blue) to create a strong visual hierarchy.
- Saturation Contrast:Use colors with different levels of saturation (e.g., bright red and muted green) to create emphasis and draw attention.
- Hue Contrast:Use colors with different hues (e.g., blue and orange) to create the most striking contrast.
Color Printing for Specific Applications
Color printing finds specialized applications in photography, graphic design, and fine art. Each domain requires tailored printing techniques and materials to achieve optimal results.
Photography
In photography, color printing is crucial for capturing and reproducing the true-to-life colors and details of an image. Professional photographers utilize high-resolution printers, specialized papers, and advanced color management systems to ensure accurate color reproduction.
Graphic Design
Graphic designers rely on color printing to create visually appealing marketing materials, brochures, and other print products. They often employ a wide range of colors, textures, and finishes to enhance the impact of their designs.
Fine Art
Fine art printing involves the reproduction of original artworks, such as paintings and drawings. This specialized field requires meticulous attention to detail, using archival-quality papers and inks to ensure the longevity and color fidelity of the printed pieces.
Future of Color Printing
The future of color printing holds exciting possibilities, driven by advancements in technology and evolving industry trends. Emerging color printing technologies, such as 3D printing and nanotechnology, are revolutionizing the way we create and interact with printed materials.
One significant trend is the increasing adoption of digital printing technologies. Digital printing offers greater flexibility, customization, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional offset printing methods. This trend is expected to continue, with digital printing becoming even more accessible and efficient in the future.
Emerging Color Printing Technologies
Emerging color printing technologies are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in the industry. 3D printing, for example, allows for the creation of three-dimensional objects with intricate color details, opening up new possibilities for prototyping, manufacturing, and artistic expression.
Nanotechnology is another promising area of research. By manipulating materials at the nanoscale, scientists are developing new types of inks and printing processes that can produce highly accurate and vibrant colors. These advancements have the potential to revolutionize the printing industry, enabling the creation of high-quality prints with enhanced durability and color accuracy.
Market Landscape and Key Players
The color printing market is highly competitive, with established players such as HP, Canon, and Epson dominating the industry. However, emerging companies are also making their mark, introducing innovative technologies and cost-effective solutions.
The market landscape is expected to shift in the future, with a growing emphasis on sustainability and eco-friendly printing practices. Companies that can develop and implement sustainable printing solutions will gain a competitive advantage in the years to come.
Implications for Businesses
The future of color printing has significant implications for businesses. Digital printing technologies are making it easier for companies to produce high-quality prints in-house, reducing costs and lead times.
Businesses can also leverage emerging technologies, such as 3D printing, to create innovative products and marketing materials that stand out in the marketplace. The ability to produce vibrant and accurate colors will be crucial for businesses looking to make a lasting impression on their customers.
Examples of Color Printing Applications

Color printing has revolutionized numerous industries, enabling businesses and individuals to create stunning and impactful visual materials. Here are some remarkable examples showcasing the versatility and impact of color printing:
Marketing and Advertising
- Brochures and flyers with vibrant images and eye-catching designs that capture attention and promote products or services.
- Posters and billboards with high-quality color reproduction that make a bold statement and reach a wide audience.
- Product packaging with vibrant colors and intricate designs that differentiate products and enhance shelf appeal.
Fine Art and Photography
- Art prints and reproductions that capture the essence of original artworks with accurate color representation and fine details.
- Photographic prints that showcase the beauty and emotion of captured moments with stunning color reproduction and sharpness.
- Limited edition prints that are highly sought after by collectors and art enthusiasts.
Education and Healthcare
- Educational materials with colorful illustrations and diagrams that make learning engaging and memorable.
- Medical charts and anatomical models with accurate color reproduction that aid in diagnosis and surgical procedures.
- Patient education materials with clear and concise color-coded information that promotes understanding and adherence to treatment plans.
Textile and Fashion
- Printed fabrics with vibrant colors and intricate patterns that add style and personality to clothing, home décor, and accessories.
- Fashion magazines with high-quality color printing that showcases the latest trends and inspires readers.
- Textile samples with accurate color representation that enable designers to make informed decisions and avoid costly mistakes.
Methods for Designing Color Printing Layouts

Creating visually appealing and effective color printing layouts requires an understanding of design principles, layout techniques, and color theory. This guide will provide insights into designing impactful color printing materials, considering various printing processes and color reproduction aspects.
Principles of Design and Layout for Color Printing
Design principles such as balance, contrast, emphasis, and unity guide the arrangement of elements in a layout. Color plays a crucial role in creating visual hierarchy, drawing attention to specific areas, and conveying messages. Understanding the principles of color theory, including color harmonies, contrast, and saturation, is essential for effective color printing.
Impact of Printing Processes on Color Reproduction
Different printing processes, such as offset printing, digital printing, and inkjet printing, have varying capabilities in reproducing colors. Offset printing offers high-quality color reproduction, while digital printing provides flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Inkjet printing is suitable for small-scale printing with vibrant colors.
Understanding the limitations and strengths of each process helps optimize color reproduction.
When printing in color, it is important to ensure that the printer is set to the correct settings for the type of paper being used. Once the printer is set up correctly, the user can then print the document. If the user wants to print an entire web page, they can use the “Print Entire Web Page” feature in their browser.
This feature allows the user to print the entire web page, including all of the text, images, and links. how to print entire web page For more information on how to print in color, please consult the printer’s manual.
Examples of Well-Designed Color Printing Layouts
Examining examples of well-designed color printing layouts can provide inspiration and guidance. Analyze successful layouts to identify effective use of color, typography, and layout techniques. Note how color is used to create visual interest, convey messages, and enhance the overall impact of the printed material.
Step-by-Step Guide to Designing a Color Printing Layout
- Define the purpose and target audience of the printed material.
- Choose a color palette that aligns with the message and brand identity.
- Plan the layout to create a visually appealing and organized arrangement.
- Use typography effectively to enhance readability and visual interest.
- Proofread the layout carefully before printing to ensure accuracy and effectiveness.
Table: Key Principles of Color Printing Layout Design, How to print colour print
| Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| Balance | Distribute elements evenly to create a visually stable layout. |
| Contrast | Use contrasting colors to create visual interest and emphasis. |
| Emphasis | Draw attention to important elements through color, size, or placement. |
| Unity | Combine elements harmoniously to create a cohesive overall design. |
Glossary of Terms Related to Color Printing Layout Design
- Bleed: Extending colors or images beyond the edge of the paper to create a seamless effect.
- CMYK: Color model used in printing, consisting of cyan, magenta, yellow, and black inks.
- DPI: Dots per inch, a measure of the resolution of printed images.
- Kerning: Adjusting the spacing between characters to improve readability and visual appeal.
- Leading: Adjusting the vertical space between lines of text to enhance readability.
Procedures for Preparing Files for Color Printing
Preparing files for color printing requires careful attention to file formats, color profiles, and resolution to ensure accurate and vibrant prints. This section guides users through the process, discusses key settings, and provides troubleshooting tips.
File Formats
- TIFF (Tagged Image File Format):A lossless format that preserves all image data, suitable for high-quality printing.
- JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group):A lossy format that compresses images, reducing file size but potentially introducing artifacts.
- PNG (Portable Network Graphics):A lossless format that supports transparency, suitable for logos and graphics.
- PDF (Portable Document Format):A universal format that can embed color profiles and fonts, ensuring consistent printing across platforms.
Color Profiles
Color profiles define the color space used in an image and how it should be interpreted by the printer. Common color profiles include:
- sRGB:A standard color space for web and general use.
- Adobe RGB:A wider color space suitable for professional printing.
- CMYK:A color space used in printing, representing Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (Black).
Resolution
Resolution determines the sharpness and detail of the printed image. The required resolution depends on the printing method and desired quality:
| Printing Method | Recommended Resolution |
|---|---|
| Inkjet | 300-600 dpi |
| Laser | 600-1200 dpi |
| Offset | 1200-2400 dpi |
Troubleshooting
- Color mismatch:Ensure the correct color profile is used and the printer is calibrated.
- Blurry or pixelated prints:Check the resolution settings and ensure the image is at least the size it will be printed.
- Incorrect colors:Verify the color mode of the image and the printer settings.
- Banding:Use a higher resolution or consider dithering to smooth color transitions.
Automation Script
To automate the file preparation process, a script can be used to perform the following tasks:
- Convert images to the desired file format.
- Assign the appropriate color profile.
- Set the resolution based on the printing method.
- Check for common errors and provide warnings.
By following these procedures and using the provided troubleshooting tips, users can effectively prepare files for color printing, ensuring accurate and professional-looking results.
FAQs
What are the different types of color printing methods?
The most common color printing methods include inkjet, laser, and thermal printing. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to choose the one that best suits your needs.
How can I ensure accurate color reproduction in my prints?
Color management is crucial for achieving accurate color reproduction. This involves using color profiles to calibrate your printer and monitor, ensuring that the colors you see on your screen are accurately represented in your prints.
What type of paper should I use for color printing?
The type of paper you use can significantly impact the quality of your prints. For best results, choose a paper that is specifically designed for color printing. This type of paper will have a smooth surface and a high brightness level, which will help to produce vibrant and accurate colors.