What is collate in printer? Collation in printing refers to the process of gathering, aligning, and assembling printed pages in the correct order to create a complete document. It ensures that the pages are arranged in the intended sequence, making it easier to read and navigate the printed material.
The collation process involves several steps, including gathering the printed sheets, jogging them to align them properly, and binding them together using various methods such as stapling, gluing, or stitching. Collation plays a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy and quality of printed documents, especially in high-volume printing operations.
Definition of Collation
Collation in the context of printing refers to the process of arranging and assembling printed sheets in the correct order to create a complete document or book. It involves gathering and organizing individual pages or sections of a printed work, ensuring they are in the proper sequence and orientation.
Collation plays a crucial role in the production of printed materials, ensuring the final product is complete, coherent, and easy to navigate. Without proper collation, the printed document would be disorganized, making it difficult for readers to follow the content or find specific information.
Purpose of Collation

Collation, in the context of printing, plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper order and assembly of printed pages. It is a post-press process that involves gathering and arranging the printed sheets in the correct sequence to create a complete and cohesive document.Collation ensures that the printed pages are assembled in the intended order, as determined by the page numbering or other sequencing system.
This is especially important for documents with multiple sections, chapters, or other divisions, where the order of pages is essential for conveying the intended information. Without proper collation, the document may become disorganised, confusing, or even unusable.
Benefits of Collation
- Ensures the correct order of printed pages, facilitating easy reading and comprehension.
- Prevents the misplacement or omission of pages, maintaining the integrity of the document.
- Simplifies the binding process, allowing for efficient and accurate assembly of the final product.
- Enhances the overall quality and professionalism of the printed document.
Types of Collation: What Is Collate In Printer
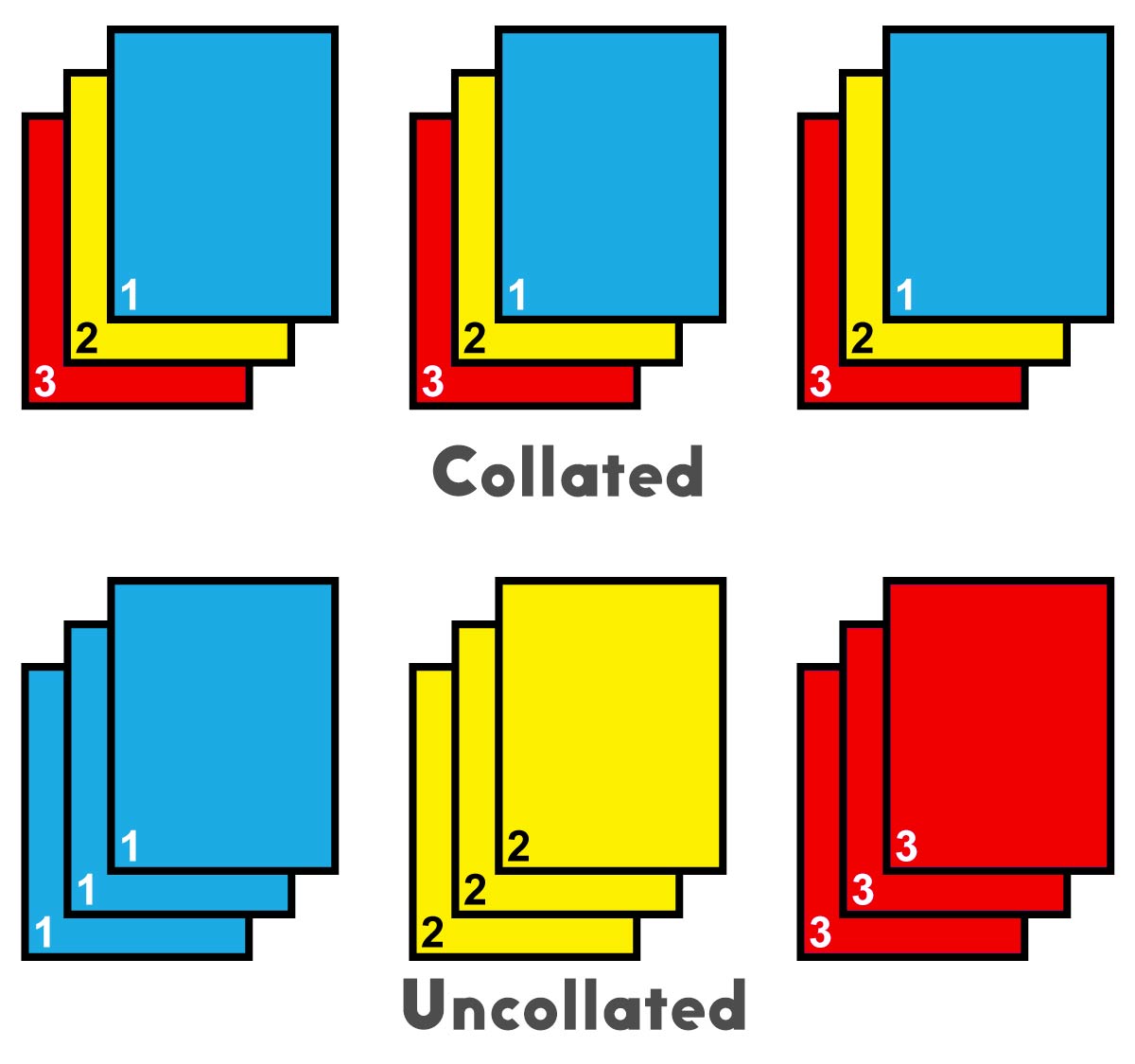
Collation in printing refers to the process of assembling and arranging printed sheets in a specific order to create a complete document or book. There are various types of collation methods used in printing, each with its own advantages and applications.
Manual Collation
- Involves manually assembling printed sheets in the correct order, typically by hand or using a simple collation device.
- Suitable for small print runs or when precise alignment and order are crucial.
Semi-Automatic Collation
- Utilizes machines to assist in the collation process, such as gathering machines or saddle stitchers.
- Faster than manual collation and can handle larger print runs.
- Requires operator intervention for loading and unloading sheets.
Automatic Collation
- Employs fully automated machines that perform the entire collation process, including gathering, folding, and binding.
- Highly efficient and suitable for high-volume printing.
- Requires minimal operator intervention.
Tower Collation
- A specific type of automatic collation where sheets are stacked vertically in towers and then collated using a rotating arm.
- Provides high accuracy and speed.
- Used for high-volume printing of books and magazines.
Perfect Binding Collation
- Involves collating sheets and binding them together with a layer of glue along the spine.
- Creates a professional and durable finish.
- Suitable for books, manuals, and other publications.
Collation Equipment

Collation is a process of gathering and arranging printed sheets in the correct order for binding. The machinery and equipment used for collation play a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy and efficiency of this process.The primary types of collation equipment include:
- Gatherers:Gatherers are machines that automatically collect and assemble printed sheets from multiple sources into sets. They can handle a wide range of paper sizes and weights, and can be programmed to produce specific sequences and combinations of sheets.
- Joggers:Joggers are used to align and square the edges of printed sheets before they are gathered. This ensures that the sheets are properly aligned for binding and prevents misfeeds.
- Inserters:Inserters are machines that insert preprinted materials, such as covers, inserts, or promotional materials, into the gathered sets of printed sheets.
- Stitchers:Stitchers are used to bind the gathered and inserted sheets together using staples or wire. They can handle a variety of binding styles, including saddle stitching, perfect binding, and wire-o binding.
- Trimmers:Trimmers are used to cut the edges of the bound sets to the desired size and shape. They can also be used to create special effects, such as rounded corners or die-cut shapes.
The proper selection and use of collation equipment is essential for producing high-quality printed materials. By automating the collation process, businesses can reduce labor costs, improve accuracy, and increase productivity.
Collation Process
Collation is a crucial step in the printing process that involves gathering, jogging, and binding documents to create a complete and organized set. The collation process ensures that all pages are in the correct order and that the final product is ready for distribution or use.
Gathering
The gathering process involves collecting all the printed pages for a particular job. It is essential to ensure that all pages are accounted for and that they are organized in the correct sequence. This can be done manually or using automated gathering machines.
Proper organization during gathering is crucial to avoid errors and ensure that the final product is complete and accurate.
Jogging, What is collate in printer
Jogging is the process of aligning the edges of a stack of papers to ensure that they are even and aligned. This step is important to prevent misalignment during binding and to ensure that the final product has a professional appearance.
Jogging can be done manually or using a jogging machine.
Binding
Binding is the final step in the collation process and involves securing the pages together to create a complete document. There are various binding methods available, including stapling, saddle stitching, perfect binding, and spiral binding. The choice of binding method depends on factors such as the number of pages, the desired durability, and the intended use of the document.
Quality Control in Collation

Quality control is paramount in collation to ensure the accuracy and completeness of the finished product. This involves implementing measures to prevent errors and maintaining high standards throughout the collation process.Methods used to ensure accuracy include:
- Establishing clear and detailed collation instructions.
- Using automated collation equipment with built-in error detection systems.
- Implementing manual verification processes to double-check the accuracy of the collated materials.
- Regularly calibrating and maintaining collation equipment to prevent errors caused by mechanical failures.
- Training operators on proper collation techniques and emphasizing the importance of accuracy.
Collation in Digital Printing

Collation plays a crucial role in digital printing processes, ensuring that printed sheets are assembled and arranged in the correct order. Digital technologies have significantly influenced collation methods, introducing automation, efficiency, and versatility.
Impact of Digital Technologies
Digital printing technologies have brought about several key advancements in collation methods:
- Automated Sheet Feeding:Digital printing presses often incorporate automated sheet feeders that precisely align and transport printed sheets to the collation station, minimizing manual intervention and errors.
- Variable Data Printing:Digital printing allows for variable data printing, where each printed sheet can contain unique information or graphics. Collation systems can be programmed to assemble sheets based on specific data fields, ensuring accurate and personalized document creation.
- On-Demand Printing:Digital printing enables on-demand production of printed materials, eliminating the need for large print runs and storage. Collation systems can quickly and efficiently assemble small batches of documents, reducing waste and improving responsiveness to customer needs.
– Describe the challenges and techniques used for collation in large-scale printing operations, such as aligning, sorting, and assembling printed sheets.
In large-scale printing operations, collation poses significant challenges due to the high volume and precision required. Aligning, sorting, and assembling printed sheets accurately and efficiently is crucial to ensure the quality and integrity of the final product.
One of the key challenges is maintaining alignment during the collation process. Misaligned sheets can lead to errors in the final assembly, affecting the overall quality of the printed product. Techniques such as optical registration systems and precision guides are employed to ensure accurate alignment of sheets before they are collated.
Sorting is another critical aspect of collation in large-scale printing. Printed sheets need to be sorted based on specific criteria, such as page number, sequence, or content. Automated sorting machines equipped with sensors and computer vision systems are used to perform high-speed sorting with a high degree of accuracy.
Finally, assembling the sorted sheets into the correct order is essential. This involves techniques such as saddle stitching, perfect binding, and adhesive binding, depending on the specific requirements of the printed product. Automated binding machines are used to ensure consistent and efficient assembly, minimizing the risk of errors.
– Elaborate on the challenges posed by the varying paper stocks and substrates used in specialty printing.
Specialty printing often involves a wide range of paper stocks and substrates, each with its unique properties and handling requirements. This diversity poses challenges for collation, as different materials may have varying thicknesses, textures, and sensitivities to handling. For instance, delicate papers like rice paper or handmade papers require careful handling to avoid tearing or creasing.
Similarly, thick or textured papers can be difficult to align and sort accurately, increasing the risk of misprints or errors.
Substrate-Specific Considerations
To address these challenges, printers must carefully consider the specific properties of each substrate used. They may need to adjust collation equipment settings, such as tension and feed mechanisms, to accommodate different paper stocks. Additionally, they may employ specialized techniques, such as hand-collating or using interleaving sheets, to protect delicate materials.
Collation in printing refers to the process of arranging printed pages in the correct order. This process ensures that the pages are assembled in a sequential manner, allowing for easy reading and comprehension of the document. For a deeper understanding of the term “collate,” visit what does collate mean printer for further information on its significance in the printing process.
Advanced Binding Techniques
Advanced binding techniques, such as Japanese stab binding and clamshell boxes, play a crucial role in preserving and presenting valuable printed materials. Japanese stab binding, with its exposed thread stitching, not only adds a decorative element but also allows the book to lay flat when opened, making it ideal for art books or portfolios.
Clamshell boxes, with their rigid construction and custom-fitted interiors, provide excellent protection for rare or fragile prints, ensuring their longevity.
Collaboration and Communication
Collaboration between printers, artists, and conservators is essential to ensure the longevity and artistic integrity of specialty prints. Printers must understand the artist’s vision and the conservator’s requirements to select appropriate materials and techniques. This collaboration helps preserve the artistic intent while ensuring the print’s physical integrity over time.
Collate in a printer is a feature that allows the printer to gather multiple copies of a document into a single set. This can be useful for creating booklets or other documents that require multiple copies of the same pages.
To use the collate feature, you will need to install a printer driver that supports collating. Once the printer driver is installed, you can select the collate option in the printer’s settings. The printer will then print multiple copies of each page of the document, and gather them into a single set.
Collation in Packaging

Collation plays a crucial role in the packaging industry, contributing to cost reduction, improved efficiency, and enhanced product protection. By collating multiple items or components into a single unit, businesses can streamline packaging processes and minimize material waste.
Collation contributes to efficient and secure packaging through various methods such as shrink wrapping, banding, and strapping. Shrink wrapping involves enclosing products in a thin plastic film that is heated to shrink and conform to the shape of the items, providing protection and tamper evidence.
Banding involves securing products together using paper or plastic bands, while strapping employs straps or tapes to bundle items securely.
Types of Collation Equipment
Various types of collation equipment are available to meet the needs of different packaging operations.
- Automatic collators: These machines automate the collation process, handling high volumes of items with precision and speed.
- Semi-automatic collators: These collators combine manual and automated processes, offering flexibility and cost-effectiveness for smaller-scale operations.
- Manual collators: These devices require manual operation and are suitable for low-volume or specialized collation tasks.
Industries Using Collation
Collation is widely used in various industries, including:
- Food and beverage: Collation is used to package food items such as snacks, beverages, and confectionery.
- Pharmaceuticals: Collation is employed to package medications, medical devices, and other pharmaceutical products.
- Electronics: Collation is used to package electronic components, such as circuit boards and cables.
Environmental Impact
Collation can have an environmental impact due to the materials used and the potential for waste generation. However, by optimizing collation processes and using sustainable materials, businesses can minimize their environmental footprint. For example, biodegradable or recyclable materials can be used for shrink wrap or banding, reducing plastic waste.
Collation in Document Management
Collation plays a crucial role in document management systems (DMSs) by organizing and retrieving documents efficiently, ensuring their accessibility and usability.
Benefits of Collation in DMSs
- Enhanced organization:Collation allows documents to be grouped and arranged in a logical order, making it easier to locate and retrieve specific documents.
- Improved efficiency:By organizing documents into collated sets, users can quickly access multiple related documents simultaneously, saving time and effort.
- Reduced errors:Collation helps prevent errors by ensuring that all relevant documents are included in a set, reducing the risk of missing or misplaced documents.
- Increased compliance:Collation facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements by organizing documents in a way that meets specific standards or guidelines.
Challenges of Collation in DMSs
- Document complexity:Complex documents with multiple pages, attachments, and revisions can pose challenges for collation, requiring careful organization and tracking.
- Data volume:Large volumes of documents can make collation time-consuming and resource-intensive, especially when dealing with unstructured data.
- Metadata management:Effective collation relies on accurate and consistent metadata, which can be challenging to maintain across large document collections.
Best Practices for Collation in DMSs
- Establish clear collation rules:Define specific rules for grouping and ordering documents to ensure consistency and efficiency.
- Use automated tools:Leverage software tools that automate collation processes, saving time and reducing errors.
- Monitor and maintain collation quality:Regularly review and update collation rules and processes to ensure their effectiveness and accuracy.
Benefits of Collation
Collation, the process of gathering and assembling printed sheets in the correct order, offers numerous benefits across various industries. It enhances efficiency, accuracy, and overall quality while reducing costs.
Improved Efficiency
Collation streamlines the printing process by automating the gathering and sequencing of printed sheets. This eliminates manual labor and reduces the time required for post-press operations, increasing productivity and allowing businesses to meet tight deadlines.
Enhanced Accuracy
Collation ensures that printed sheets are assembled in the correct order, minimizing errors and improving the accuracy of printed materials. Automated collation systems utilize advanced technology to verify sheet counts and alignment, reducing the risk of human error and ensuring consistent quality.
Superior Quality
By eliminating manual handling and minimizing errors, collation contributes to the overall quality of printed materials. Well-collated documents and products enhance customer satisfaction and reflect professionalism.
Cost-Effectiveness
Collation can save businesses money by reducing labor costs and minimizing waste. Automated collation systems operate efficiently, reducing the need for manual labor and overtime. Additionally, accurate collation minimizes the need for reprints and reworks, saving on material and production costs.
Potential Drawbacks
While collation offers significant benefits, it may have some potential drawbacks:
- Equipment Costs:Automated collation systems can be expensive to purchase and maintain.
- Space Requirements:Collation equipment requires dedicated space within the production facility.
- Complexity:Some collation systems can be complex to operate and require specialized training.
Future Trends in Collation
The future of collation is expected to be shaped by advancements in technology, particularly in the areas of automation, data management, and artificial intelligence (AI).
AI-Driven Collation Automation
AI-powered systems are increasingly being used to automate collation processes, including:
Automated sheet alignment
AI algorithms can analyze scanned images of printed sheets to detect and correct misalignments, ensuring accurate collation.
Intelligent sorting
AI-driven systems can classify and sort printed sheets based on predefined criteria, such as size, color, or content, improving the efficiency and accuracy of the collation process.
Self-adjusting collation lines
AI-powered systems can monitor collation line performance and make real-time adjustments to optimize throughput and minimize errors.
Cloud-Based Collation Services
Cloud-based collation services offer a range of benefits, including:
Remote access
Cloud-based services allow users to access and manage collation processes from anywhere with an internet connection.
Scalability
Cloud services can be scaled up or down to meet changing demand, providing flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
Centralized data management
Cloud-based services provide a central repository for collation data, enabling real-time monitoring and analysis.
Real-Time Data Collation and Analysis
Real-time data collation and analysis can provide valuable insights into collation processes, including:
Performance monitoring
Real-time data can be used to monitor collation line performance, identify bottlenecks, and improve overall efficiency.
Quality control
Data analysis can help identify and mitigate quality issues, ensuring the production of high-quality collated materials.
Predictive maintenance
Real-time data can be used to predict potential maintenance issues and schedule maintenance proactively, minimizing downtime.
FAQs
What is the purpose of collation in printing?
Collation ensures that printed pages are arranged in the correct order, making it easier to read and navigate the document.
What are the different types of collation methods?
There are various collation methods, including manual, semi-automatic, and fully automated, each with its own advantages and applications.
What equipment is used for collation?
Collation equipment includes gatherers, joggers, and binders, which work together to align, assemble, and bind printed pages.